Are you looking for a material that is both strong and light? Standard metals often force you to compromise, being too heavy or corrosive. Titanium rods offer the perfect solution.
A titanium rod is a solid bar made from titanium metal or its alloys. It is famous for its high strength-to-weight ratio1, excellent corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility, making it essential for advanced industries.
My name is Zhang Wei. I’m a senior R&D engineer here in Baoji, China’s Titanium Valley. Every day, I work with these amazing materials. To truly understand a titanium rod, you need to know more than just what it is. You need to see what it can do. This is where the real value becomes clear.
What is a titanium rod used for?
Choosing the right material for a critical job is tough. A bad choice can lead to equipment failure and expensive problems. Titanium rods provide reliability in demanding applications.
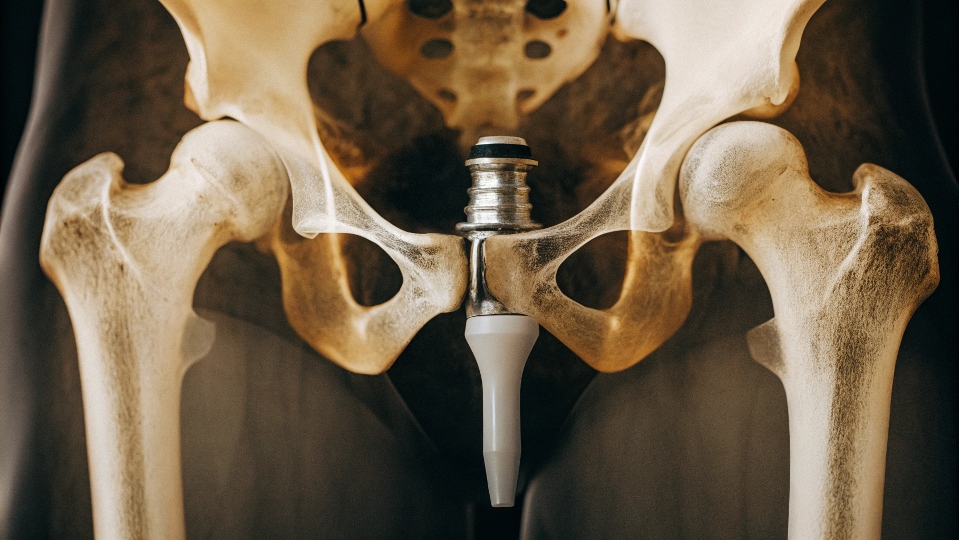
Titanium rods are primarily used in aerospace for aircraft frames and engines. They are also essential in the medical field for surgical implants, like hip joints. Their corrosion resistance makes them perfect for chemical processing2 and marine industries.
When product managers like Lisa ask me about applications, I break it down into key areas. Each area takes advantage of a specific property of the metal.
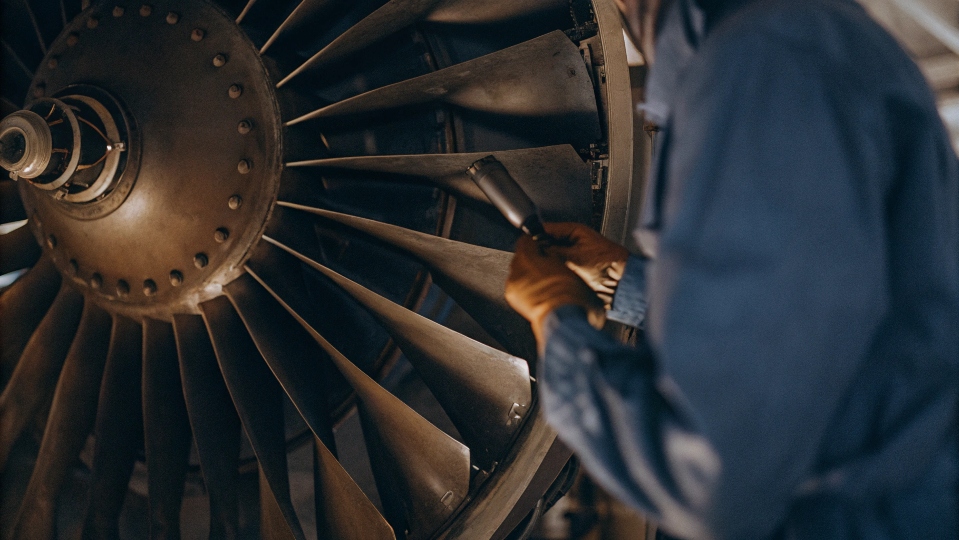
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace, every gram matters. Titanium has an incredible strength-to-weight ratio. This means we can build strong parts that are much lighter than steel ones. I’ve worked on projects developing specific alloys for landing gear components and engine fan blades. These parts must handle extreme stress and temperatures. Using titanium helps improve fuel efficiency and allows aircraft to carry heavier payloads safely. It is the go-to material when performance cannot be compromised.
Medical and Surgical
Titanium’s biggest advantage here is biocompatibility. It does not cause a reaction in the human body. The U.S. National Institutes of Health confirms it’s one of the best metals for this. Bone can actually grow and fuse directly to a titanium implant. This process is called osseointegration3. It creates a very strong and stable bond. This makes it ideal for hip and knee replacements, dental implants, and bone screws.
What does titanium do to your body?
Thinking about putting metal inside your body can be scary. Some metals cause allergies or are rejected by the body. Titanium is different, offering a safe and reliable solution.
Inside the body, titanium is extremely safe and non-reactive. It is biocompatible, meaning your tissues will not have a negative reaction to it. Bone cells recognize its surface and grow directly onto it, creating a strong, permanent bond for implants.
The question of how titanium behaves in the body is critical, especially for medical devices. The answer lies in its unique surface chemistry.
The Power of the Oxide Layer
When titanium is exposed to air or water, it instantly forms a very thin, stable, and tough layer of titanium oxide on its surface. This layer is passive and non-reactive. It acts as a protective barrier. It prevents the metal from corroding or leaching ions into the body. This is why titanium does not cause the allergic reactions we sometimes see with other metals like nickel or cobalt. This passive layer is the key to its biocompatibility.
Osseointegration: A Unique Bond
This biocompatibility allows for a special process called osseointegration. It means the bone literally integrates with the titanium. Unlike other materials that form a fibrous tissue layer around them, bone cells attach directly to the titanium oxide surface. I often explain to clients that this is like a tree root growing into an object, making it part of the structure. This creates an incredibly durable and long-lasting foundation for dental implants and joint replacements.
What are 5 uses for titanium?
You know titanium is a high-performance material. But where exactly is it used? Its cost can make you question if it’s really necessary. Let’s look at five key applications.
Five main uses for titanium are: 1. Aerospace parts like aircraft frames and engines. 2. Medical implants such as hip and knee joints. 3. Chemical processing equipment. 4. High-performance sports gear4 like bicycle frames. 5. Marine hardware for ships and submarines.
I often use a simple table to show clients like Lisa the wide range of uses. It helps connect each application to the main reason why titanium is the best choice for the job. This helps justify the material selection, both in terms of performance and cost. Each use highlights a different strength of the metal. For example, in sports gear, both strength and low weight are important. In chemical plants, its resistance to corrosion is the most vital property. This versatility is what makes titanium so valuable.
| Application Area | Key Property Used | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Aerospace | High Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Aircraft fuselage, landing gear, engine parts |
| 2. Medical | Biocompatibility, Corrosion Resistance | Hip and knee implants, dental implants, bone screws |
| 3. Industrial | Superior Corrosion Resistance | Heat exchangers, desalination pipes, reaction vessels |
| 4. Consumer & Sports | Lightweight, High Strength, Aesthetics | Bicycle frames, golf clubs, high-end watches, jewelry |
| 5. Marine | Resistance to Saltwater Corrosion | Submarine hulls, propeller shafts, onboard hardware |
Are titanium rods strong?
You need a material that is incredibly strong, but also lightweight. Usually, you have to choose one or the other. Titanium gives you both strength and low weight.
Yes, titanium rods are exceptionally strong. Alloys like Ti-6Al-4V have a strength-to-weight ratio that is much higher than most steels. This means a titanium rod can provide the same strength as a steel rod while weighing almost half as much.
"Strong" can mean different things. When engineers talk about strength, we often look at the strength-to-weight ratio. This is where titanium really shines.
Looking for Reliable Titanium Bars?
Our titanium bars are available in various grades and specifications to meet the highest industry standards. Perfect for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications, ensuring quality and performance under the toughest conditions.

Understanding Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Imagine you have a bar of titanium and a bar of steel. Both can support 1,000 kilograms before they break. The steel bar is heavy. The titanium bar is much lighter. Titanium gives you the same strength for about 45% less weight compared to steel. This is its key advantage. For a product manager like Lisa, this translates to huge benefits in applications like aerospace, where less weight means more fuel efficiency and better performance. This is why we say titanium is incredibly strong for its weight.
How it Compares to Steel
Let’s look at some numbers. This table helps to show the difference clearly. I use this to explain why choosing a titanium alloy is a smart engineering decision for high-performance needs.
| Property | Common Steel | Titanium Alloy (Grade 5) |
|---|---|---|
| Density (Weight) | High (~7.8 g/cm³) | Low (~4.4 g/cm³) |
| Tensile Strength | Good (~400 MPa) | Excellent (~950 MPa) |
| Strength-to-Weight | Moderate | Very High |
As you can see, the Grade 5 titanium alloy is more than twice as strong as common steel, but it is much lighter. This combination is what makes it a premium material.
Conclusion
Titanium rods are a superior material. They are strong, light, and resistant to corrosion. These features make them crucial for advanced aerospace, medical, and industrial applications worldwide.
-
Explore the importance of this ratio in material selection for engineering projects. ↩
-
Discover the role of titanium in enhancing the efficiency and safety of chemical processes. ↩
-
Explore the process of osseointegration and its role in successful implant surgeries. ↩
-
Learn how titanium enhances the performance and durability of high-end sports equipment. ↩