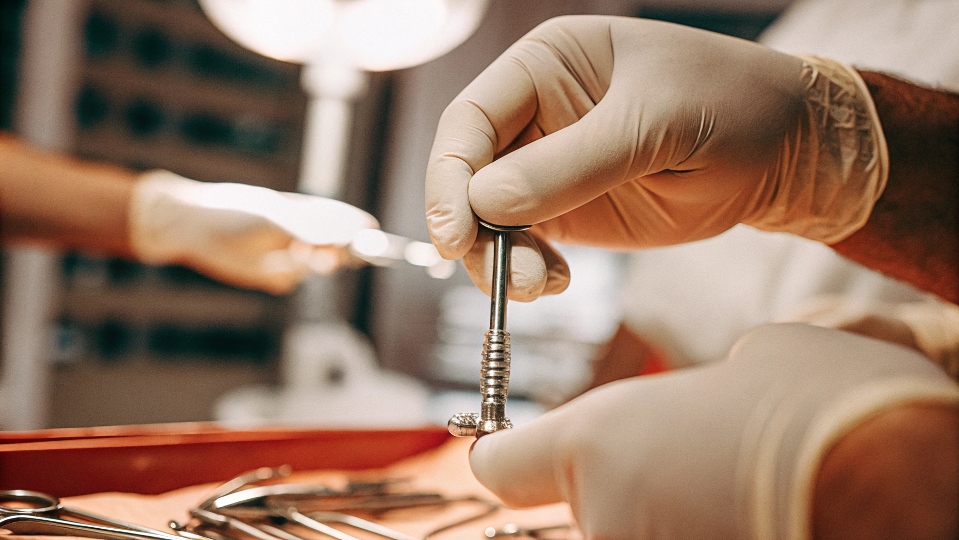
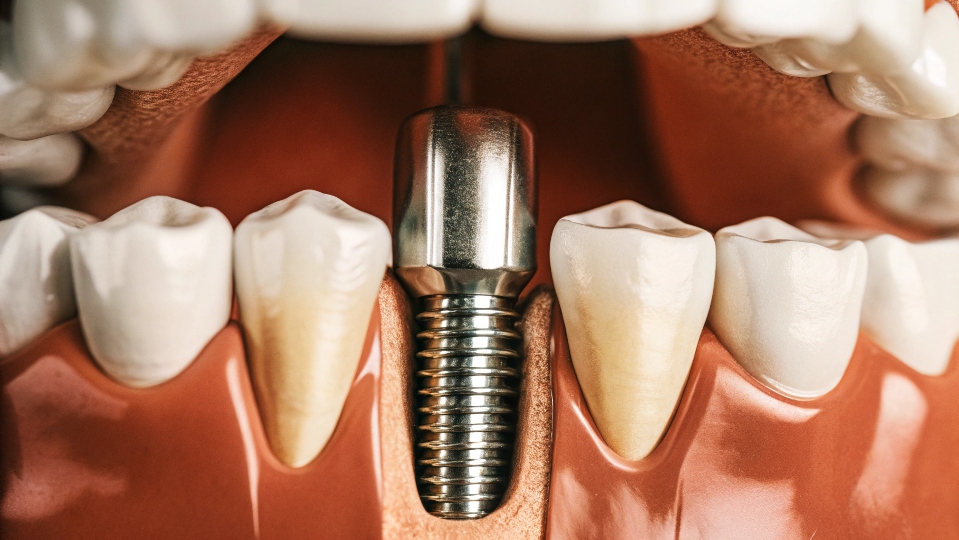
Мысли о медицинской операции и так вызывают стресс. Когда вы слышите слово "имплантат", вы беспокоитесь о том, что ваш организм отторгнет его, что приведет к еще большим болям и проблемам в дальнейшем.
Титан - лучший выбор для медицинских имплантатов, поскольку он обладает высокими биосовместимый1Это означает, что он не вызывает негативной реакции в организме. Он также обладает уникальной способностью, называемой остеоинтеграция2Кость человека естественным образом растет и срастается с ним, создавая прочное, постоянное соединение.
Эта тема глубоко личная для многих конечных пользователей моих клиентов. Хотя я обычно обсуждаю титан для аэрокосмической или промышленной промышленности с такими менеджерами по закупкам, как Дэвид, принципы надежности и безопасности материала универсальны. Для медицинского применения ставки наиболее высоки. Качество жизни пациента зависит от безупречной работы имплантата на протяжении десятилетий. За годы работы я убедился, что уникальные свойства титановых сплавов обеспечивают спокойствие как хирургам, так и пациентам. Давайте рассмотрим, почему этот металл является золотым стандартом для устройств, устанавливаемых внутри человеческого тела.
Для каких медицинских имплантатов используется титан?
Вы знаете, что имплантат может быть в вашем будущем. Но вы, возможно, не совсем понимаете, какие именно устройства изготавливаются из титана и как они могут улучшить ваше здоровье.
Титан используется для широкого спектра распространенных медицинских имплантатов. К ним относятся зубные имплантаты для замены зубов, замена суставов3 для бедер и коленей, спинномозговые кейджи4Костные пластины и винты, используемые для фиксации переломов. Он также используется в кардиостимуляторы5.
Список областей применения велик, потому что титан решает сразу столько задач. Для зубных имплантатов его способность срастаться непосредственно с челюстной костью создает основу, такую же прочную, как естественный зубной корень. В ортопедии его прочность обеспечивает правильное заживление сломанной кости при поддержке пластины и винтов. При замене суставов он обеспечивает прочную и долговечную новую поверхность для движения. Это не просто случайный выбор материала; в каждом случае титан выбирается потому, что его свойства идеально соответствуют требованиям работы, обеспечивая лучшие результаты для пациентов и долгосрочный успех.
Распространенные медицинские устройства и почему титан подходит для них
| Тип имплантата | Конкретное использование | Почему титан идеален |
|---|---|---|
| Ортопедические имплантаты | Тазобедренные/коленные суставы, костные винты, пластины | Высокая прочность, выдерживающая вес тела и движения; отличная биосовместимость. |
| Зубные имплантаты | Замена корней зубов | Остеоинтеграция создает постоянное, стабильное соединение с челюстной костью. |
| Спинальные имплантаты | Стержни, стержни, винты | Обеспечивает жесткую поддержку для стабилизации позвоночника во время сращения; противостоит усталости. |
| Черепные пластины | Исправление переломов черепа | Прочные, но легкие, обеспечивают защиту без лишнего веса. |
| Корпуса для кардиостимуляторов | Корпус электронных компонентов | Он инертен, защищая устройство от попадания жидкостей в организм, а организм - от устройства. |
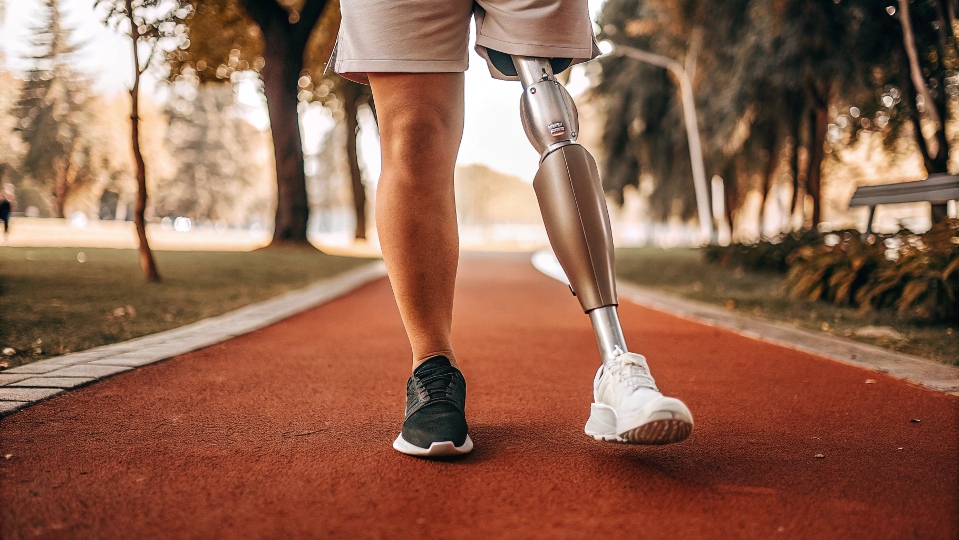
Почему титан широко используется в медицине, например, в протезировании?
Представьте себе протез, который кажется тяжелым и неуклюжим. Это превращает каждый шаг в трудную задачу, ограничивает вашу подвижность и делает повседневную жизнь трудной и утомительной.
Титан широко используется в протезирование6 потому что его превосходство соотношение прочности и веса7 позволяет создавать прочные, поддерживающие конечности, которые при этом невероятно легкие. Это снижает утомляемость пользователя, повышает комфорт и обеспечивает более естественный диапазон движений.
Этот вопрос я обсуждал со многими специалистами. Известные инженеры-протезисты часто отмечают непревзойденный баланс между прочностью и весом титана, который имеет решающее значение для обеспечения мобильности пользователя и долговременного ношения. Для устройства, которое человек будет носить весь день, каждый день, важен каждый грамм. Тяжелый протез требует больше энергии для перемещения, что приводит к усталости. Титан обеспечивает необходимую структурную целостность для ходьбы, бега и повседневной деятельности без ущерба для веса. Кроме того, его свойство остеоинтеграция2 революционизирует протезирование6. Для некоторых ампутантов титановый имплантат устанавливается непосредственно в кость, что позволяет прикрепить протез конечности прямо к скелету. Это создает гораздо более прочное и стабильное соединение.
Два столпа успеха титана в протезировании
- Соотношение прочности и веса: Материал должен быть достаточно прочным, чтобы выдержать полный вес тела человека и динамические нагрузки при движении. Титан обеспечивает такую прочность при вдвое меньшем весе стали, что является огромным преимуществом для носимого устройства.
- Остеоинтеграция: Для современных протезов способность кости прирастать непосредственно к поверхности титанового имплантата создает бесшовную, мощную связь между пользователем и его протезом, улучшая контроль и сенсорную обратную связь.
Каковы побочные эффекты титановых винтов в теле?
Вставлять в тело инородный предмет вроде металлического винта - это страшно. Вполне естественно беспокоиться о долгосрочных последствиях, таких как аллергическая реакция8или другие осложнения со здоровьем.
К счастью, негативные побочные эффекты от титановых имплантатов встречаются крайне редко. Наиболее обсуждаемым потенциальным побочным эффектом является аллергическая реакция, но титан настолько биосовместим, что вероятность этого невероятно мала. Для подавляющего большинства пациентов титан абсолютно безопасен.
Безопасность пациентов является приоритетом номер один, и данные по титану весьма обнадеживающие. По данным клинических исследований, проведенных в клинике Майо, аллергия на титан встречается крайне редко: зарегистрировано менее 0,6% случаев при установке имплантатов. Такой замечательный показатель безопасности обусловлен стабильным, инертным оксидным слоем, который образуется на поверхности титана. Этот слой действует как барьер, не позволяя металлу вступать в реакцию с биологическими жидкостями или тканями. Хотя любая хирургическая процедура сопряжена с рисками, такими как инфекция или механическое ослабление9 имплантата, проблемы, вызванные непосредственно самим титановым материалом, практически не встречаются. Именно поэтому ему доверяют хирурги уже более 50 лет.
Взгляд на потенциальные (но редкие) проблемы
| Выпуск | Описание | Вероятность |
|---|---|---|
| Аллергическая реакция | Иммунная реакция на титановый сплав, вызывающая воспаление или боль. | Крайне редко (<0,6%) |
| Механическое ослабление | Со временем имплантат теряет прочное соединение с костью. | Нечастое явление, часто связанное с хирургическими факторами или сильным стрессом. |
| Высвобождение ионов | Микроскопические частицы металла изнашиваются в течение многих лет. | Возникает на очень низком уровне; оксидный слой титана сводит его к минимуму. |
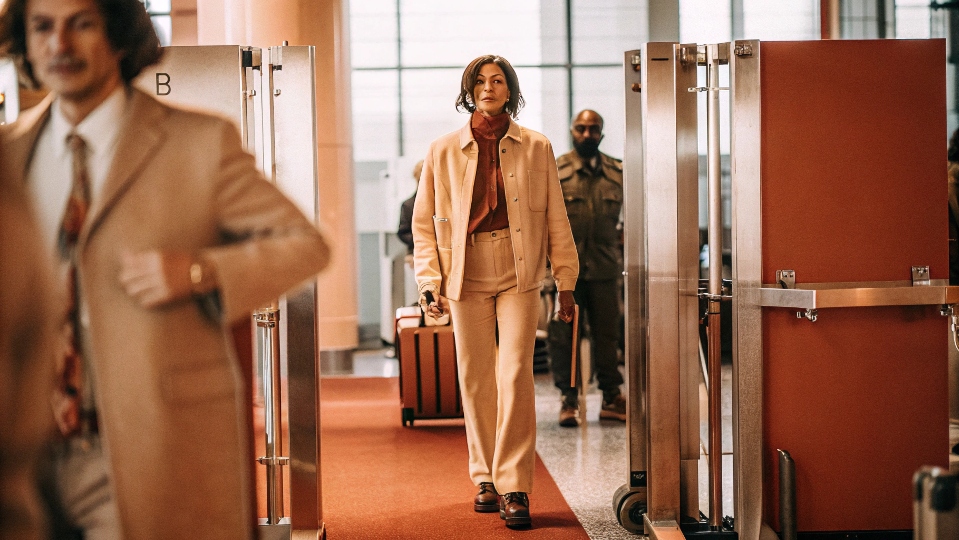
Срабатывают ли титановые медицинские имплантаты от металлоискателей?
У вас есть медицинский имплантат, и вы с ужасом ожидаете следующей поездки в аэропорт. Мысль о том, что может сработать сигнализация и вызвать задержку на посту безопасности, - распространенный источник беспокойства в поездках.
Нет, почти во всех случаях титановые медицинские имплантаты не вызывают срабатывания стандартных металлодетекторов. Титан не является ферромагнитным материалом, то есть он не магнитится и не нарушает электромагнитные поля, используемые большинством сканеров безопасности.
Этот практический вопрос мне часто задают. Ответ на него приносит значительное облегчение. Эксперты из Управления транспортной безопасности (TSA) подтверждают, что большинство титановых имплантатов медицинского класса не вызывают срабатывания стандартных металлодетекторов в аэропортах. Эти приборы предназначены для обнаружения ферромагнитных металлов, таких как железо, никель и кобальт. Поскольку титан не обладает такими магнитными свойствами, вы обычно можете пройти через них без каких-либо проблем. Правда, очень большие имплантаты, такие как полный протез бедра или колена, могут быть достаточно плотными, чтобы их могли обнаружить самые чувствительные современные сканеры, но это все равно редкость. Для небольших предметов, таких как зубные имплантаты, пластины и винты, вероятность срабатывания сигнализации практически отсутствует.
Почему титан "невидим" для большинства сканеров
| Тип металла | Ферромагнетик? | Реакция металлоискателя | Пример |
|---|---|---|---|
| Титан | Нет | Вряд ли вызовет тревогу | Тазобедренные суставы, зубные имплантаты |
| Хирургическая сталь | Часто Да | Вероятность возникновения тревоги | Старые имплантаты, некоторые винты |
| Железо/никель | Да | Включается сигнализация | Не используется в современных имплантатах |
Заключение
Титан является основным материалом для медицинских имплантатов благодаря своей безопасности, прочности и уникальной способности интегрироваться с костью, обеспечивая надежную и долговечную работу внутри человеческого тела.
-
Узнайте о биосовместимости и ее важности для обеспечения безопасности пациентов при использовании имплантатов. ↩
-
Узнайте, как остеоинтеграция повышает стабильность зубных имплантатов. ↩ ↩
-
Разберитесь в материалах, используемых для замены суставов, и их преимуществах. ↩
-
Узнайте о кейджах для спинального синтеза и их роли в стабилизации позвоночника. ↩
-
Изучите технологию, лежащую в основе кардиостимуляторов, и материалы, обеспечивающие их безопасность. ↩
-
Узнайте, как титан повышает функциональность и комфорт протезов конечностей. ↩ ↩
-
Узнайте, почему соотношение прочности и веса имеет решающее значение для работы медицинских изделий. ↩
-
Поймите редкость аллергических реакций на титан и его профиль безопасности. ↩
-
Узнайте о факторах, которые могут привести к механическому расшатыванию медицинских имплантатов. ↩